|
I am an assistant professor of computer science at the University of British Columbia, where I research quantum computation and information. Previously, I obtained my PhD from the University of Maryland under advisors Andrew Childs and Carl Miller. Before that, I obtained my BA and MMath from the University of Cambridge. Name in Chinese: 王道辰. Teaching 2025W2: CPSC 536W. |

|
|
I'm interested in the structures beneath quantum speed-ups, algorithm design, and real-world applications.
I'm also interested in quantum cryptography. Works below are listed in order of first appearance on arXiv.
|
Preprints
|
Matt Kovacs-Deak, Daochen Wang†, Rain Zimin Yang arXiv 2026 We prove the title statement, resolving a conjecture of Fortnow, Nisan, and Szegedy from 1994. |
|
Daochen Wang arXiv 2025 [Tsinghua: slides] In seeking quantum advantage for simulating quantum systems, I explain the unusual energy spectra of compressed quantum states, such as matrix product states. |
|
Amin Shiraz Gilani, Daochen Wang†, Pei Wu, Xingyu Zhou arXiv v2 2025 We study quantum graph algorithms given an edge list, making connections to basic open problems in quantum query complexity, such as k-distinctness. |
|
Vishnu Iyer, Siddhartha Jain, Robin Kothari, Matt Kovacs-Deak, Vinayak M. Kumar, Luke Schaeffer, Daochen Wang†, Michael Whitmeyer arXiv v2 2025 We prove special cases of a conjecture from the analysis of Boolean functions that has remained open for over thirty years and is connected to post-selected quantum query complexity. [Update: conjecture resolved in a paper above.] |
Publications
 |
Kelsey A. Jackson, Carl A. Miller, Daochen Wang† QIP 2025 and Eurocrypt 2024 We ground the security of the primary post-quantum digital signature scheme, standardized by NIST as ML-DSA, in the hardness of Module-LWE and Module-SIS. |
 |
Dong An, Jin-Peng Liu, Daochen Wang, Qi Zhao Communications in Mathematical Physics 2025 We prove that quantum algorithms generally work best when simulating quantum dynamics but can sometimes be fast-forwarded when simulating non-quantum dynamics. |
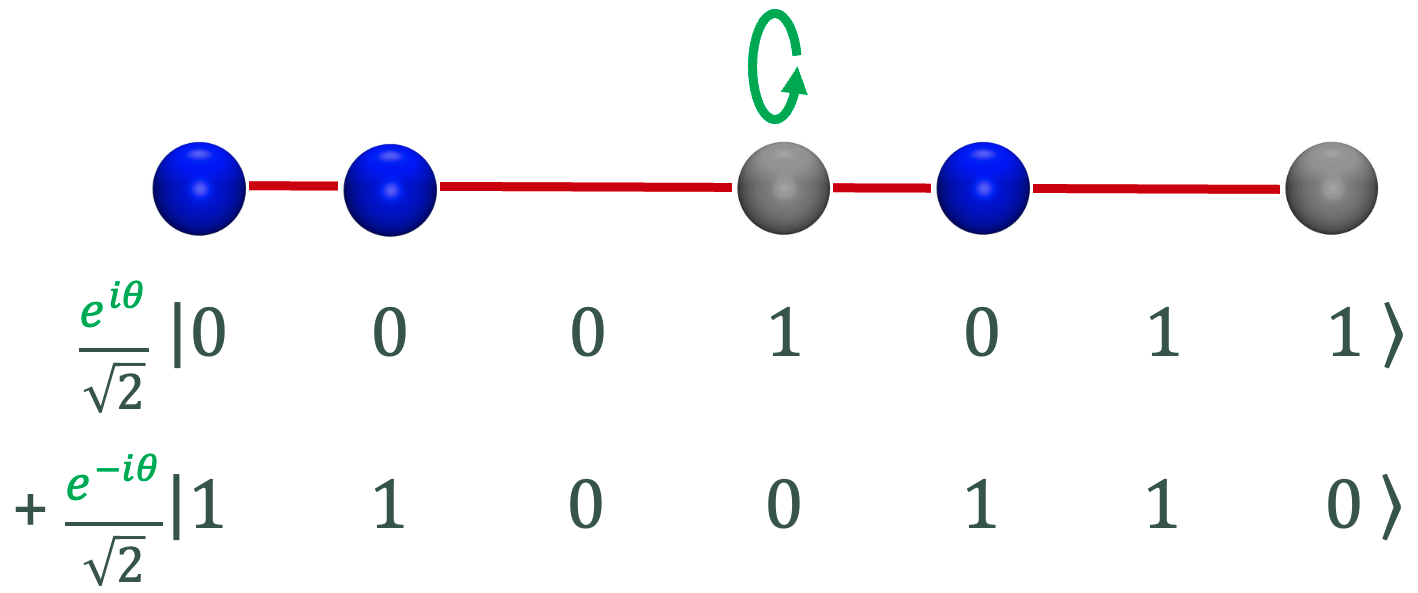 |
Yusuf Alnawakhtha, Atul Mantri, Carl A. Miller, Daochen Wang† Quantum 2024 We give a simpler proof-of-quantumness based on LWE and sketch applications to randomness generation, quantum money, and encrypted quantum simulation. |
|
|
Andrew M. Childs, Robin Kothari, Matt Kovacs-Deak, Aarthi Sundaram, Daochen Wang† ACM Transactions on Quantum Computing 2025 and QIP 2023 We quantumly speed up divide and conquer in certain settings and apply it to string problems, including longest increasing subsequence and longest common subsequence. |
 |
Honghao Fu, Daochen Wang†, Qi Zhao ICALP 2023 We show how to efficiently self-test the preparation and measurement of multiple EPR pairs assuming LWE cannot be solved quickly by quantum computers. Applications include device-independent quantum key distribution and dimension testing. |
|
|
Daochen Wang, Aarthi Sundaram, Robin Kothari, Ashish Kapoor, Martin Roetteler ICML 2021 We quantify the quantum speedups achievable for reinforcement learning in terms of calls to a generative model of the underlying Markov decision process. |
|
|
Daochen Wang*, Xuchen You*, Tongyang Li, Andrew M. Childs AAAI 2021 We construct an optimal quantum algorithm for identifying the best arm in a multi-armed bandit that is quadratically faster than any classical algorithm. |
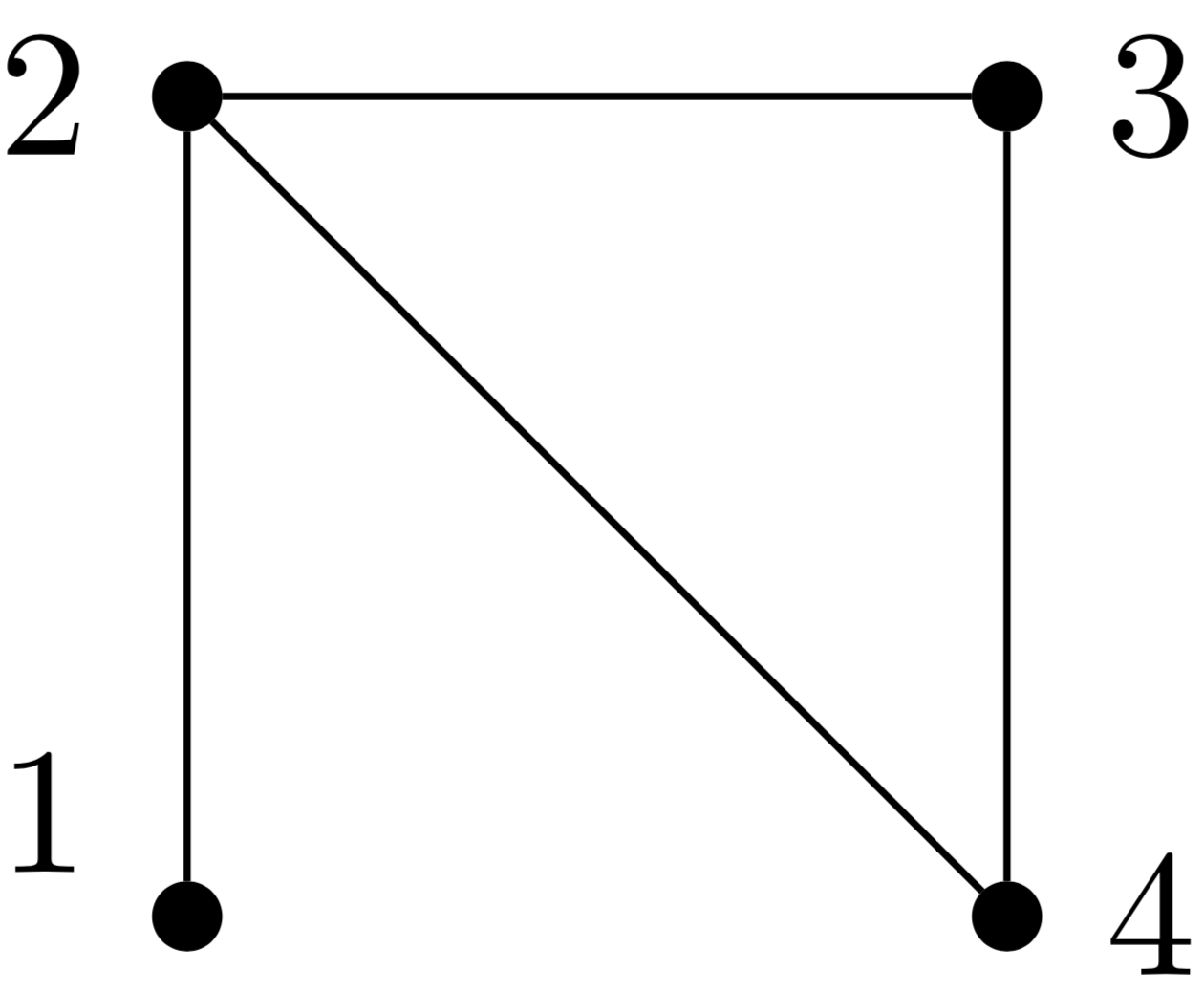 |
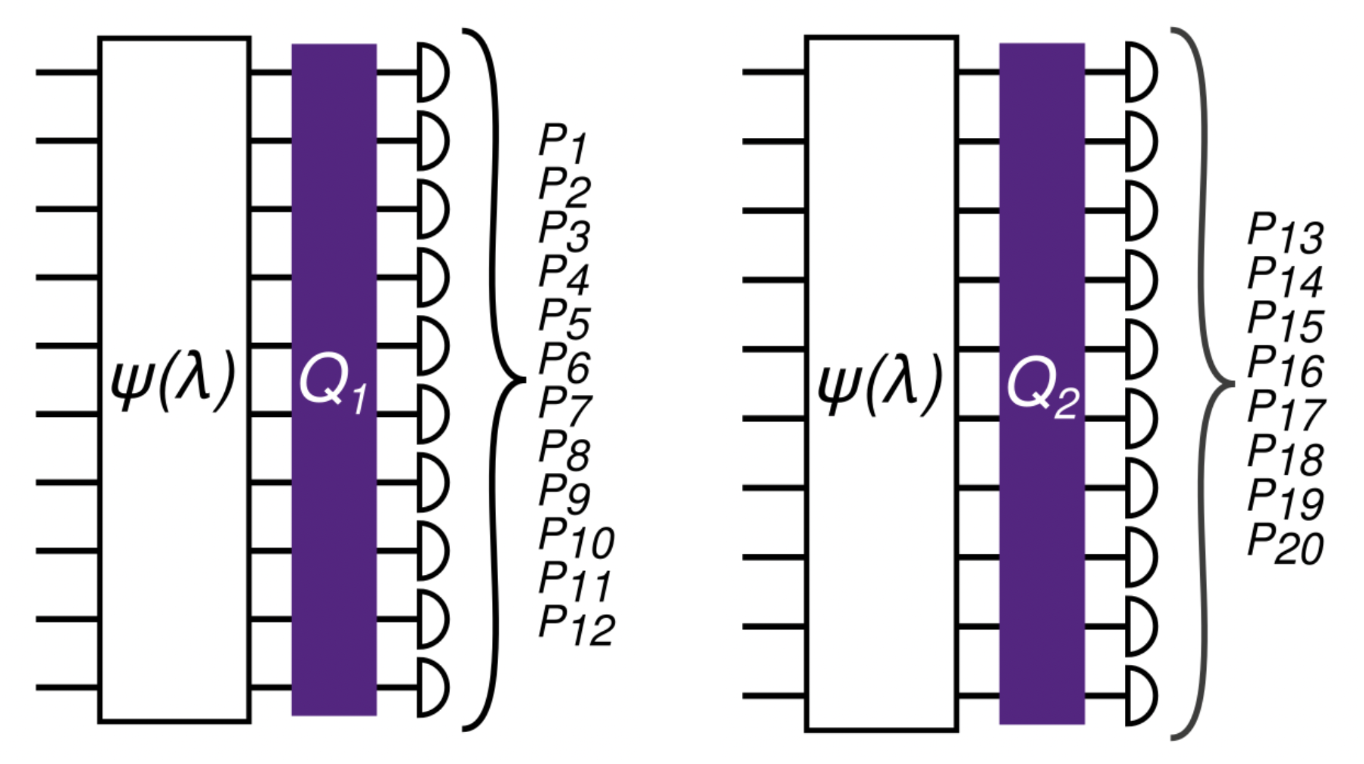
Shalev Ben-David, Andrew M. Childs, András Gilyén, William Kretschmer, Supartha Podder, Daochen Wang† SIAM Journal on Computing 2024, QIP 2021, and FOCS 2020
We characterise how a problem's symmetries determine whether quantum computation can drastically
speed up its solution; it turns out that graph symmetries play the key role.
|
 |
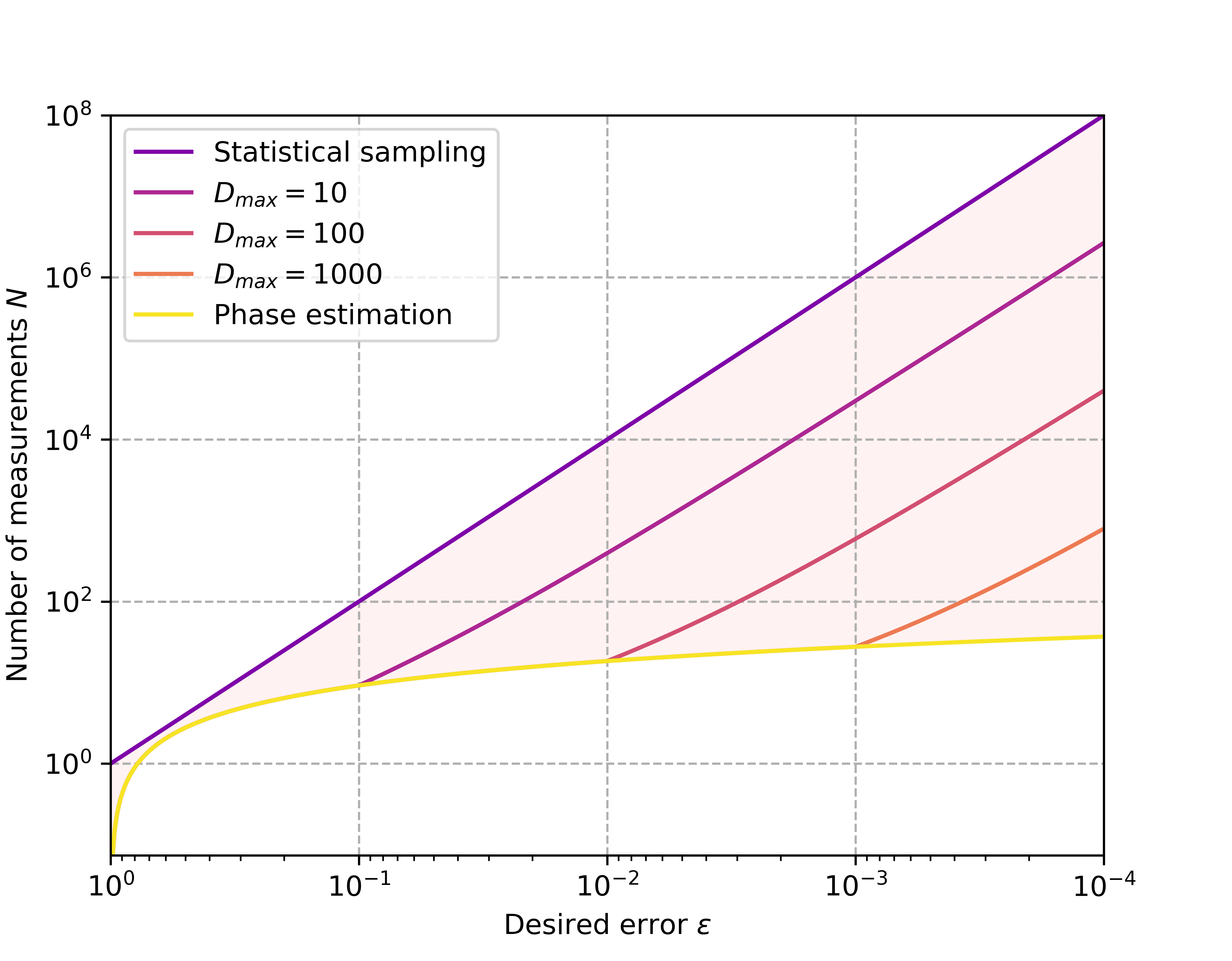
in the presence of finite sampling error Ophelia Crawford*, Barnaby van Straaten*, Daochen Wang*, Thomas Parks, Earl Campbell, Stephen Brierley Quantum 2021 We reduce the number of measurements needed to estimate the expectation value of an observable by a few orders of magnitude via simultaneous measurements. |
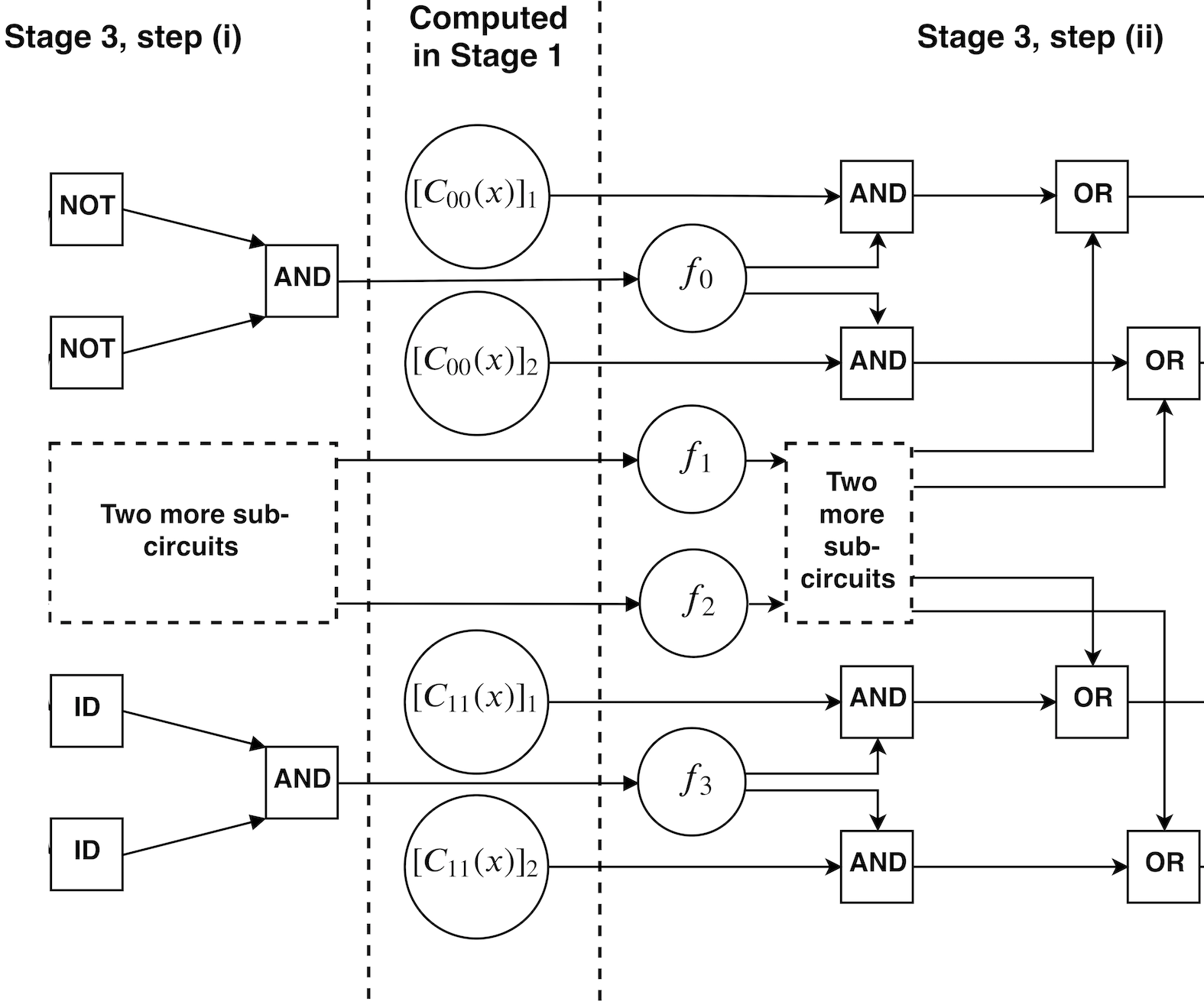 |
Daochen Wang Physical Review A 2022 I extract a notion of "p-simulation" from a breakthrough paper in 2018 and then construct explicit classical circuits that can p-simulate any quantum circuit. |
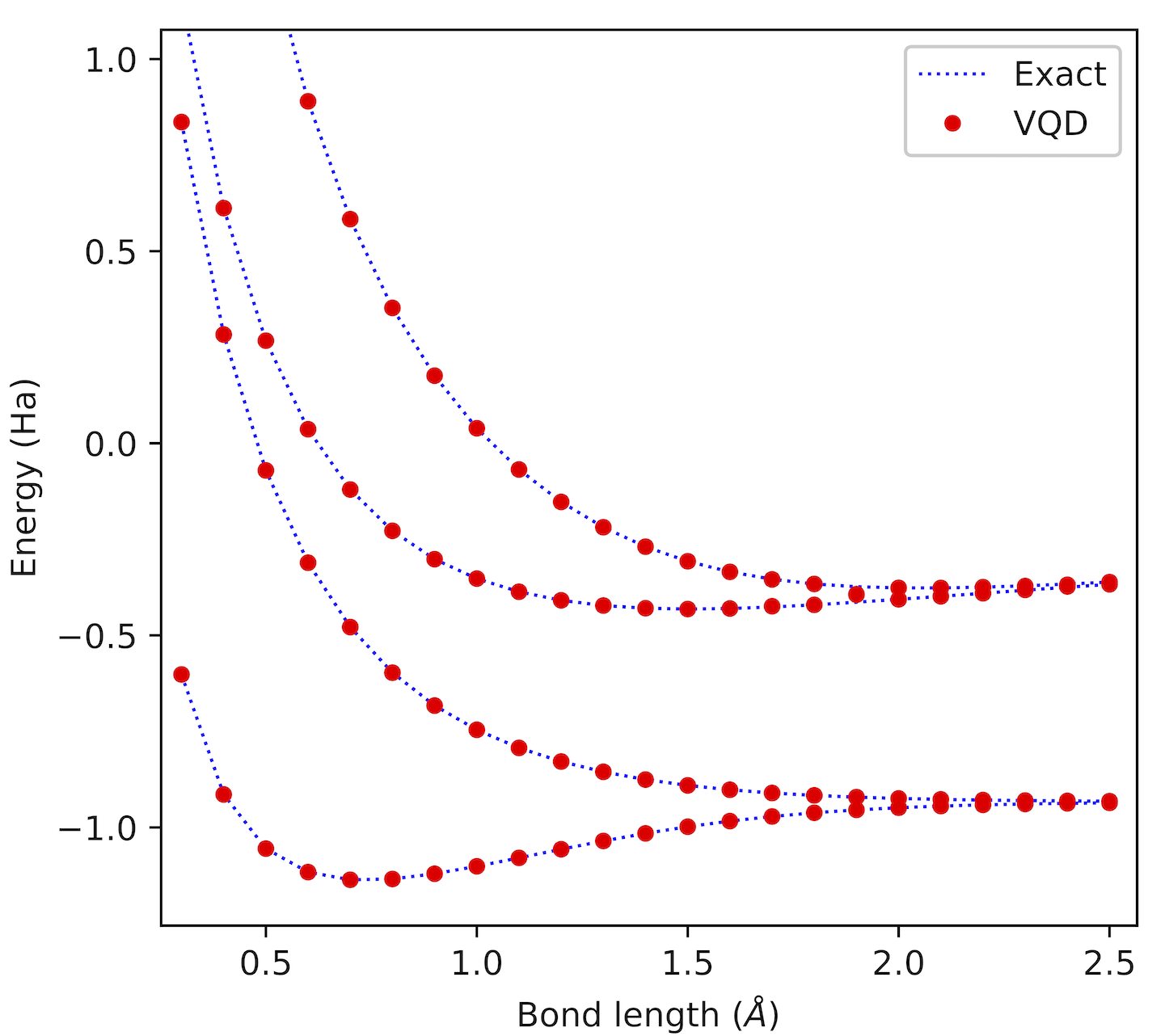 |
Oscar Higgott, Daochen Wang, Stephen Brierley Quantum 2019 We enable the variational quantum eigensolver to compute excited states at little extra cost by penalising overlaps between quantum states. Integrated into: IBM Qiskit, Xanadu PennyLane, Quantinuum InQuanto. |
 |
Daochen Wang, Oscar Higgott, Stephen Brierley Physical Review Letters 2019 We accelerate the variational quantum eigensolver by making it behave more like quantum phase estimation as more coherence time becomes available. |
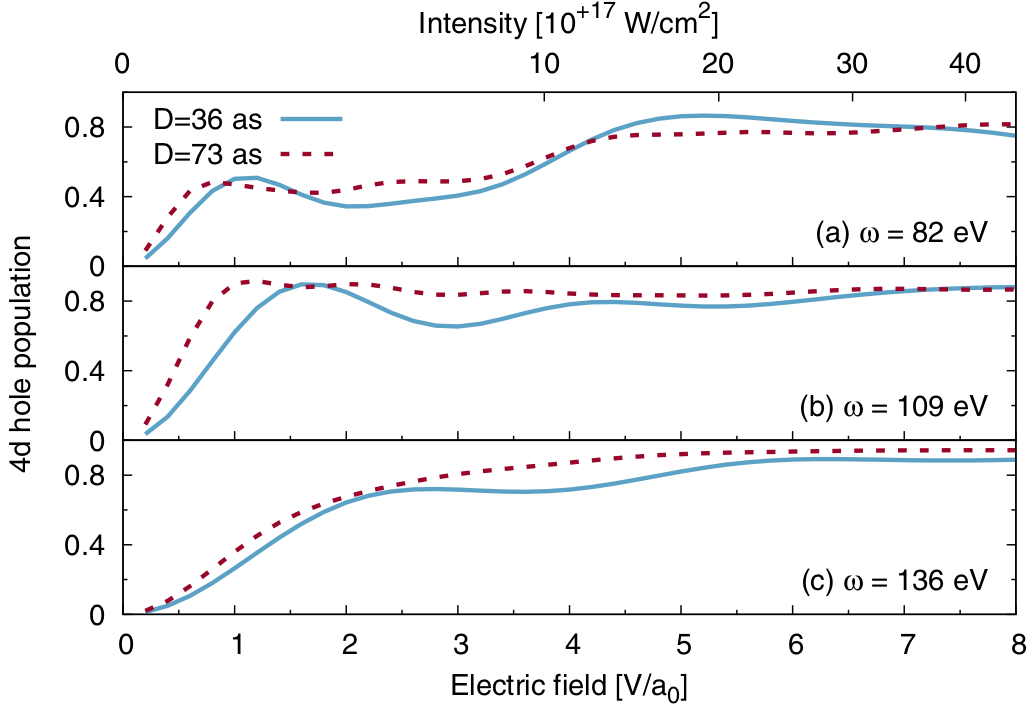 |
Stefan Pabst, Daochen Wang, Robin Santra Physical Review A 2015 We find that super-short yet super-intense pulses of light can drive Rabi oscillations between bound states of negative energy and a pseudo-bound state of positive energy. |
|
|
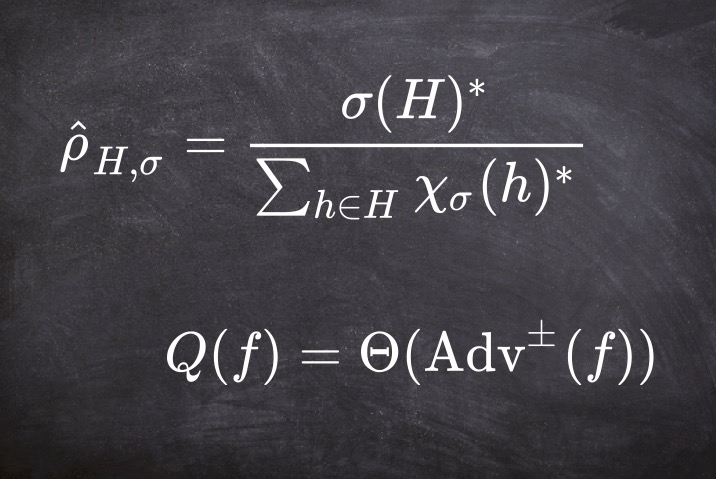 |
|
|
|
 |
Daochen Wang [slides] This is my PhD thesis, which I defended in Spring 2023. |
 |
Sandesh Kalantre, Eddie Schoute, Daochen Wang Solutions to assignment problems from lecture course CS766/QIC820 Theory of Quantum Information (Fall 2017) at Waterloo by John Watrous. These problems also appear in the book on the left. |
|
Jarrod R. McClean, Kevin J. Sung, Ian D. Kivlichan, Yudong Cao, Chengyu Dai, E. Schuyler Fried, Craig Gidney, Brendan Gimby, Pranav Gokhale, Thomas Häner, Tarini Hardikar, Vojtěch Havlíček, Oscar Higgott, Cupjin Huang, Josh Izaac, Zhang Jiang, Xinle Liu, Sam McArdle, Matthew Neeley, Thomas O'Brien, Bryan O'Gorman, Isil Ozfidan, Maxwell D. Radin, Jhonathan Romero, Nicholas Rubin, Nicolas P. D. Sawaya, Kanav Setia, Sukin Sim, Damian S. Steiger, Mark Steudtner, Qiming Sun, Wei Sun, Daochen Wang, Fang Zhang, Ryan Babbush Quantum Science and Technology 2020 I contributed code that allows you to automatically retrieve molecular geometries from the PubChem database - try: geometry_from_pubchem('water'). |
 |
Eureka is a recreational math magazine published by The Archimedeans society. This issue was published when I was the society's president a long time ago. Enjoy! |
|
Last updated: 13th January 2026
|